Fossil Mammals For Sale
Fossil Mammals For Sale – The earliest known mammals were the morganucodontids, tiny shrew-size creatures that lived in the shadows of the dinosaurs 210 million years ago.
They were one of several different mammal lineages that emerged around that time. The first mammals evolved from a population of vertebrates called therapsids (mammal-like reptiles) at the end of the Triassic period. They coexisted with dinosaurs throughout the Mesozoic Era.
We have a huge variety of mammal fossils for sale, including morganucodon teeth, mammoth teeth, early primate teeth and many more fossil mammals from around the world.
Showing 1–50 of 1033 results
-
Sold out!

Beaver Tooth for Sale – Extinct Castoroides Giant Beaver #1
$55.00 -
Sold out!

Beaver Tooth for Sale – Fossil Castor canadensis from FL #2
$20.00 -

Bison Priscus Ice Age Bison Skull from Yakutia Russia
$24,000.00 -

Bison Priscus Ice Age Bison Vertebra from Russia
$275.00 -

Bison Tooth Fossil for Sale – Extinct Bison from Florida
$30.00 -

Brontotherium Jaw from S. Dakota #1
$650.00 -
Sold out!

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #1
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #10
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #11
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #12
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #13
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #14
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #15
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #16
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #17
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #18
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #19
$75.00 -
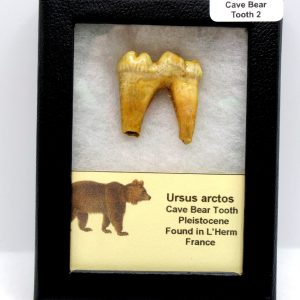
Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #2
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #20
$75.00 -
Sold out!

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #21
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #22
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #23
$75.00 -
Sold out!

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #24
$75.00 -
Sold out!

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #3
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #4
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #5
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #6
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #7
$75.00 -

Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #8
$75.00 -
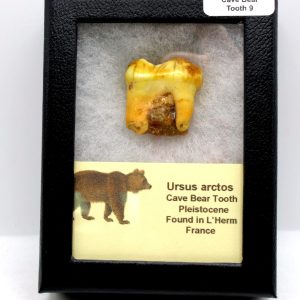
Cave Bear Tooth – L’Herm France #9
$75.00 -
Sold out!

Cetacea Fossil Miocene Dolphin Tooth from N. Carolina #1
$45.00 -
Sold out!

Cetacea Fossil Miocene Dolphin Tooth from N. Carolina #2
$45.00 -
Sold out!

Cetacea Fossil Miocene Dolphin Tooth from N. Carolina #3
$55.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #100
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #101
$5.00 -
Sold out!

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #102
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #103
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #104
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #105
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #106
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #107
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #108
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #109
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #110
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #111
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #112
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #113
$5.00 -
Sold out!

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #114
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #115
$5.00 -

Dasypus bellus Armadillo Scutes for Sale from Florida #116
$5.00
- Buy Fossils
- Fossils for Sale
- Large Selection
- Great Prices and Great Selection
- Authenticity Guaranteed
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
- Your TRUSTED SOURCE SINCE 1997!
- Many more videos are available on our YouTube Channel.
The Rise of Fossil Mammals: Evolution, Diversity & Scientific Insights
Abstract
Fossil mammals preserve a deep evolutionary narrative that extends more than 200 million years. These specimens reveal how early mammaliaforms survived mass extinctions, diversified after the fall of the dinosaurs, and evolved into the vast ecological spectrum we see today. Across global sediments, fossil mammals provide a uniquely detailed record for reconstructing ancient climates, biogeography, and ecosystem dynamics.
- Introduction: Why Fossil Mammals Matter
Mammals occupy nearly every ecological niche on Earth, from deep oceans to desert dunes. Their origins, however, trace back to small, nocturnal, shrew-like ancestors overshadowed by dinosaurs. Fossil mammals are scientifically invaluable because they:
- Document long-term evolutionary transitions, including jaw restructuring and brain expansion
- Track climate change through isotope analyses and morphological adaptations
- Reveal biogeographic dispersal routes, such as intercontinental migrations across ancient land bridges
- Provide high-resolution fossil records, especially in Cenozoic sediments where mammals dominate
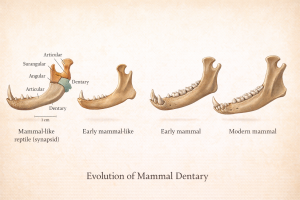
- Origins of Mammals: From Synapsids to Early Mammaliaforms
2.1 Synapsid Roots
Mammals evolved from synapsids, a lineage distinguished by a single temporal opening behind the eye socket. By the Late Permian, advanced synapsids known as therapsids exhibited mammal-like traits such as differentiated teeth (incisors, canines, post-canines) and semi-upright posture.
2.2 Defining Mammaliaforms
Early mammaliaforms, including Morganucodon and Megazostrodon, showcase key evolutionary innovations:

- Three-bone middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes)
- Precise dental occlusion enabling efficient food processing
- Endothermy onset, inferred from bone histology
These traits enhanced sensory acuity, ecological flexibility, and metabolic efficiency.
- Mammalian Expansion After the Dinosaur Extinction
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction triggered a massive ecological reset. With dinosaurs gone, mammals radiated rapidly.

3.1 The Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM)
A major warming event ~56 Ma accelerated mammalian evolution. Fossils show:
- Dwarfing events in horses (Sifrhippus)
- Rapid dispersal of primates and artiodactyls
- Expansion of forest ecosystems, shaping arboreal adaptations
3.2 Diversification of Major Mammal Groups
Post-K–Pg fossils reveal the emergence of:
- Primates with grasping hands and enhanced vision
- Cetaceans transitioning from land to sea
- Perissodactyls and artiodactyls developing specialized limbs
- Carnivorans evolving cutting carnassials and complex social behaviors
- Key Evolutionary Innovations in Mammals
4.1 Dentition and Dietary Specialization
Tooth morphology is one of the most diagnostically rich traits in mammalian paleontology:
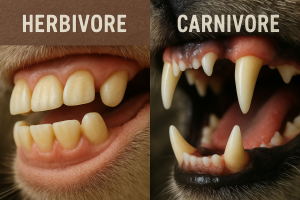
- Hypsodont teeth for grazing mammals in open grasslands
- Carnassials adapted for shearing flesh
- Multicusped molars enabling omnivory and dietary flexibility
4.2 Limb Modifications and Locomotion
Fossils illustrate transitions to:
- Cursorial running in horses and antelopes
- Powered flight in bats
- Fully aquatic locomotion in whales
4.3 Sensory and Neurological Development
Endocast studies demonstrate increased neocortical expansion and enhanced olfactory and auditory capabilities—key to adaptive success.
5. Iconic Fossil Mammals and Their Scientific Importance

5.1 Smilodon fatalis
A saber-toothed cat illustrating predator–prey dynamics in Pleistocene ecosystems.
5.2 Mammuthus primigenius
Woolly mammoths provide ice-age climate archives through tusk isotopes and stomach contents.
5.3 Paraceratherium
The largest land mammal ever discovered, showcasing extreme body size evolution.
5.4 Andrewsarchus
A mysterious carnivorous ungulate shedding light on early mesonychid and artiodactyl relationships.
- Scientific Methods in Mammalian Paleontology
Modern paleontological research integrates:
6.1 Radiometric Dating
Techniques like argon–argon (⁴⁰Ar/³⁹Ar) and uranium–lead dating establish chronological frameworks.
6.2 Stable Isotope Analysis
Carbon and oxygen isotopes reconstruct dietary habits and paleoclimate conditions.
6.3 CT Scanning & 3D Reconstruction
Digital imaging reveals internal structures—inner ears, cranial cavities, microanatomy—without damaging fossils.
6.4 Paleogenomics
In rare cases (e.g., mammoths), ancient DNA enhances evolutionary reconstructions beyond morphological inference.
- Fossil Mammals as Climate Proxies
Mammalian fossils provide environmental clues:
- Tooth enamel isotopes track aridity and vegetation changes
- Faunal turnover marks major climatic events (e.g., Miocene cooling)
- Body-size shifts correlate with Bergmann’s Rule and thermal regulation
These lines of evidence are essential for understanding long-term climate patterns.
- Biogeography: Mammal Dispersal Across Ancient Worlds
Important dispersal events include:
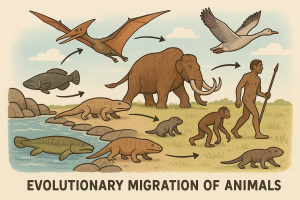
- The Great American Biotic Interchange (GABI)
- Beringian crossings by early horses, mammoths, and humans
- Afro-Eurasian exchanges that shaped carnivore and herbivore communities
These migrations reveal how continents, climates, and species co-evolved.
- Future Directions in Mammalian Paleontology
Emerging research focuses on:
- Machine learning for fossil classification
- Paleoenvironmental modeling integrating big data
- Synchrotron imaging of microstructures
- Improved ancient DNA recovery in Pleistocene contexts
These technologies promise more precise evolutionary histories and species-level resolution.
Conclusion
Fossil mammals illuminate a remarkable evolutionary journey from small synapsid ancestors to the dominant megafauna of the Cenozoic and the diverse species of today. Their fossil record—rich in anatomical detail and chronological resolution—continues to refine our understanding of biodiversity, climate change, and ecological adaptation. As analytical technologies advance, fossil mammals remain a cornerstone of evolutionary science and a vital resource for reconstructing Earth’s deep past.
Buy Fossils from Prehstoric Fossils with Confidence. Authenticity Guaranteed!