Description
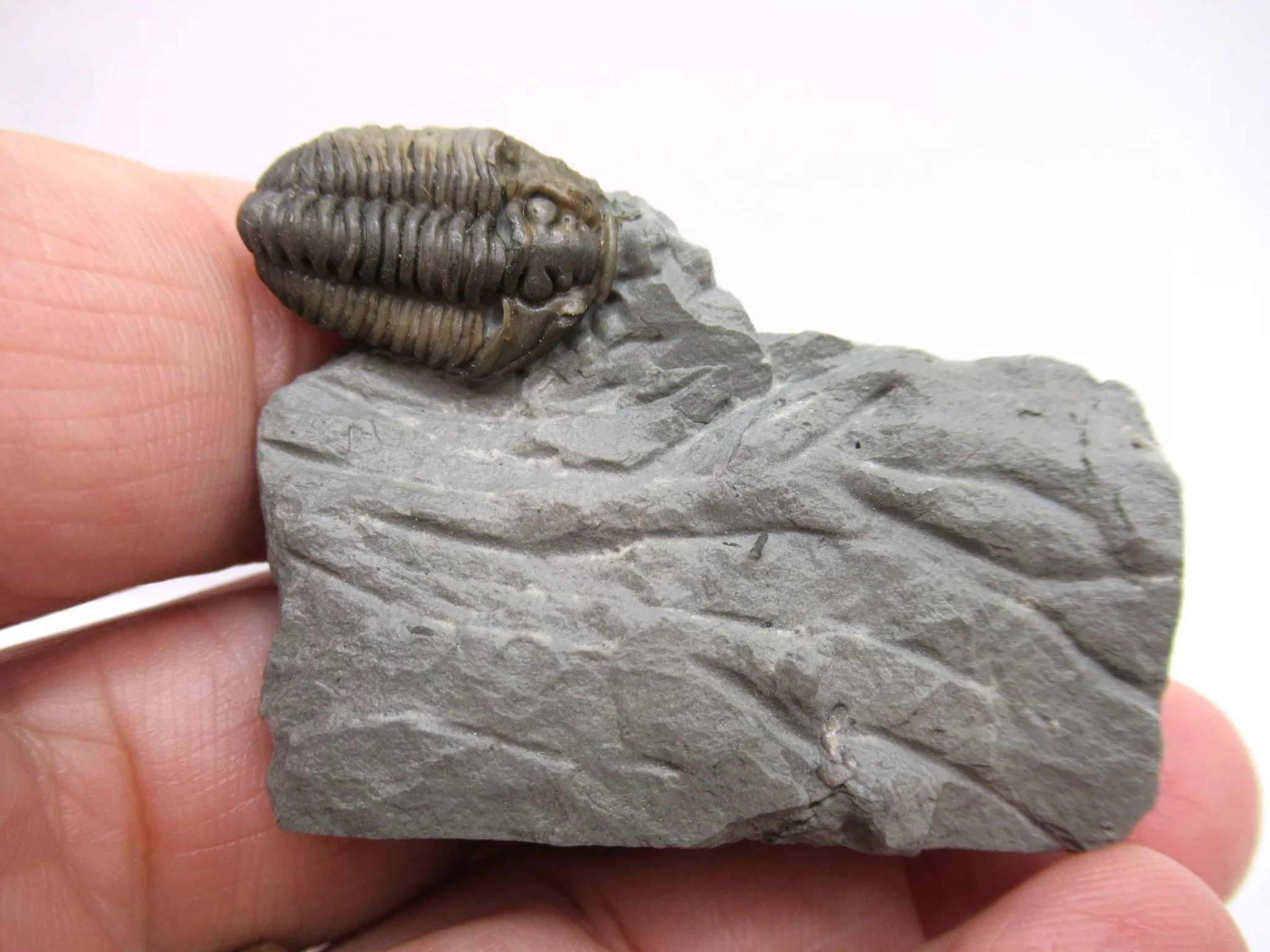
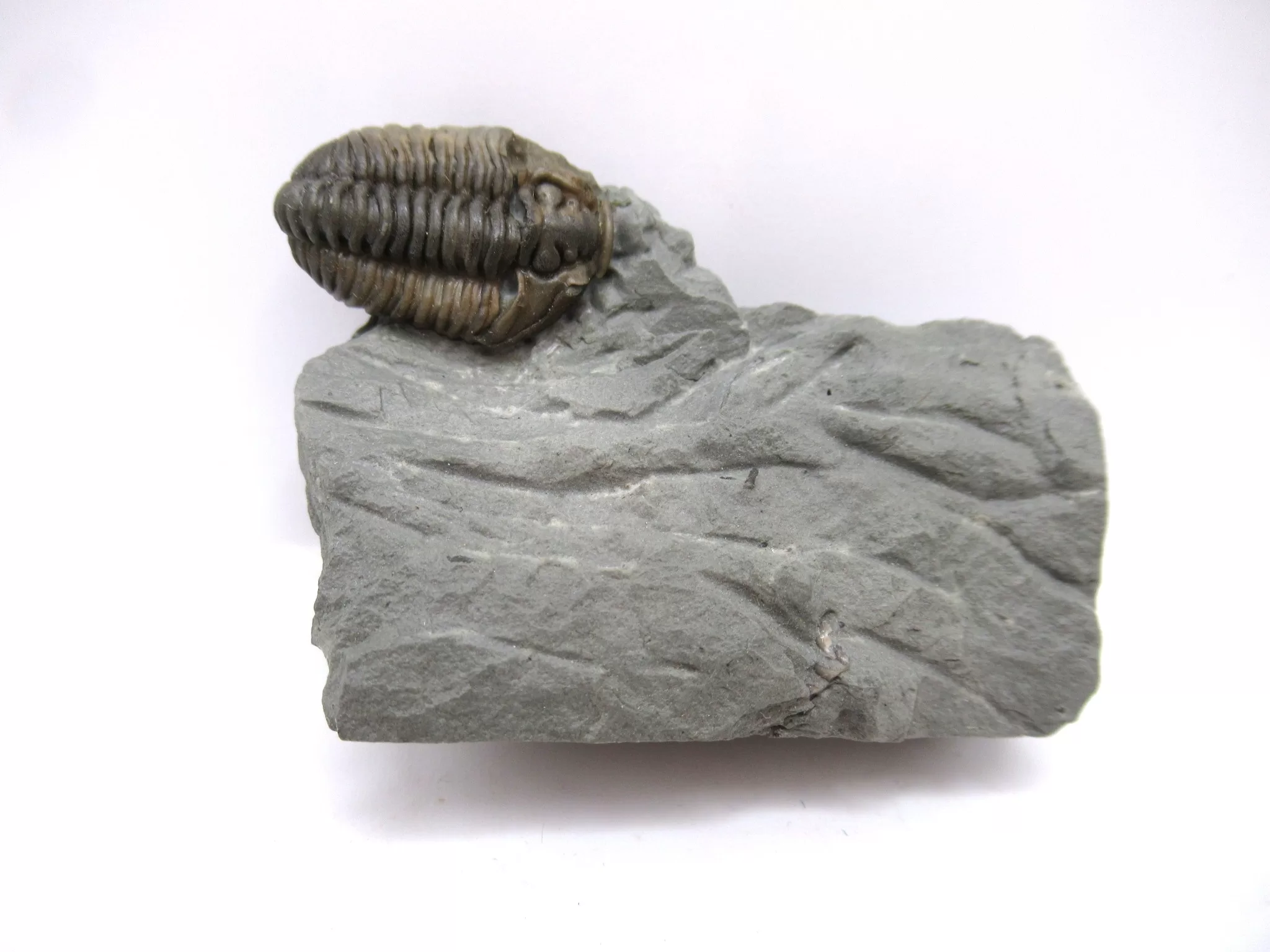
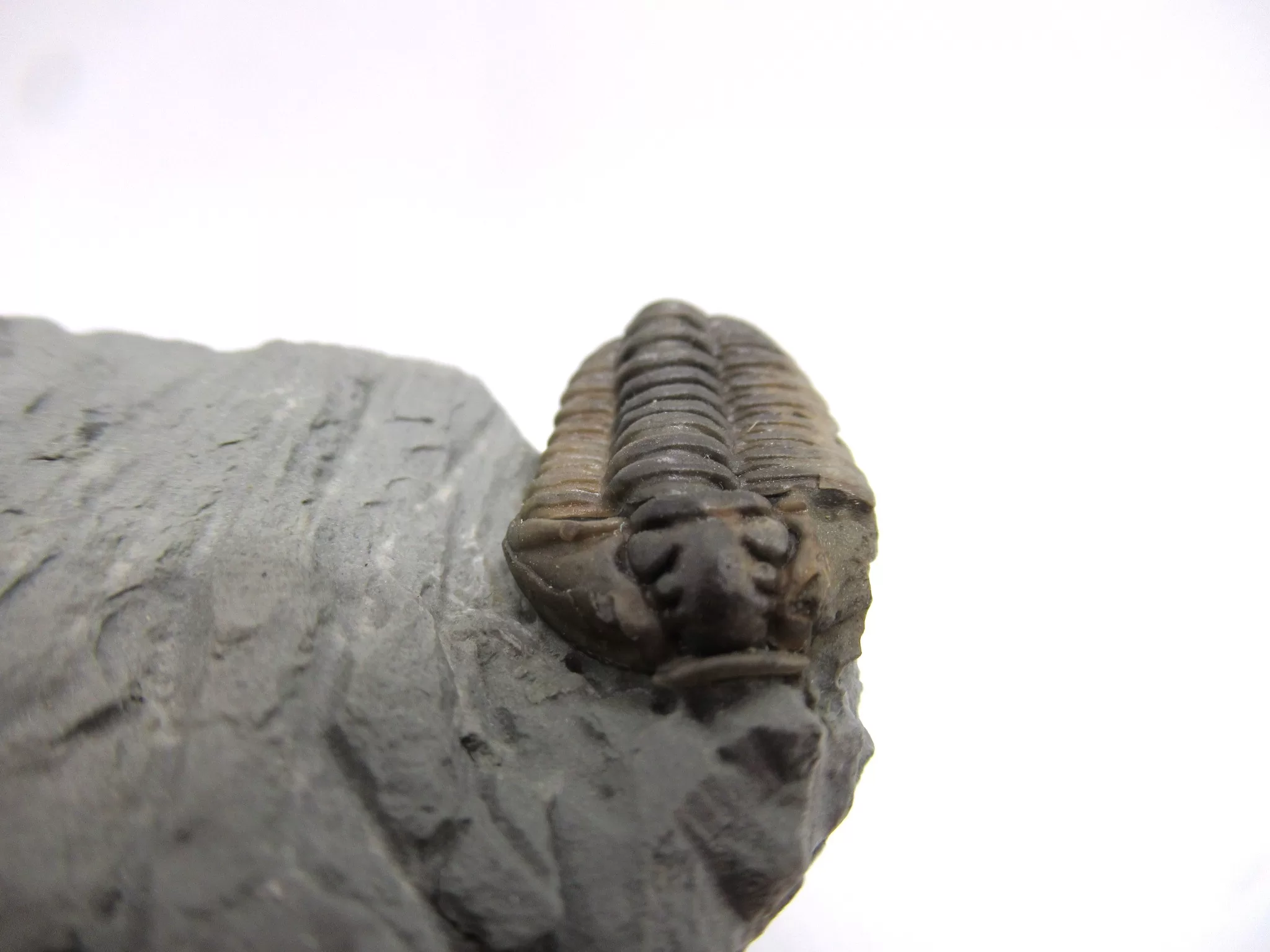
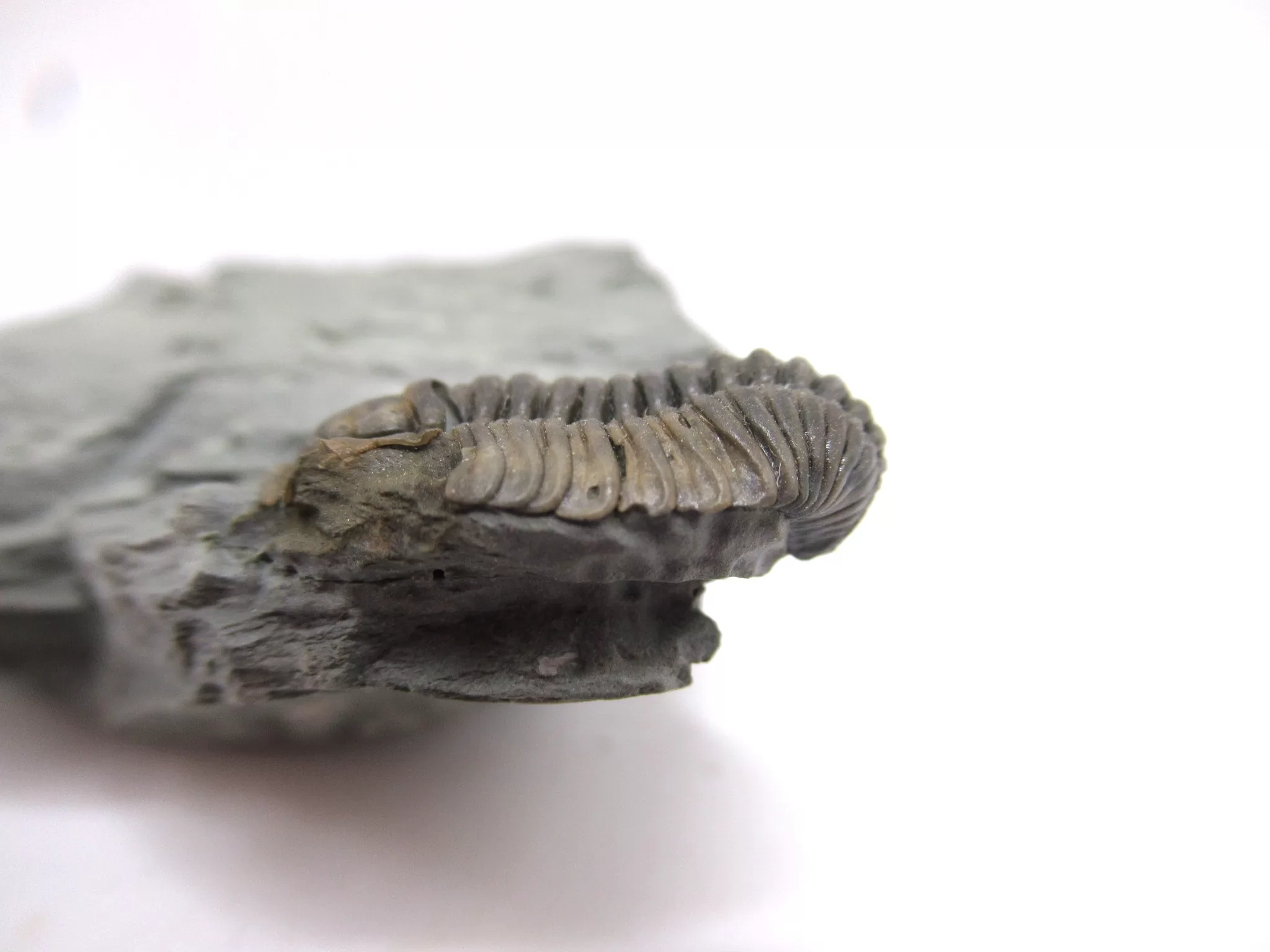
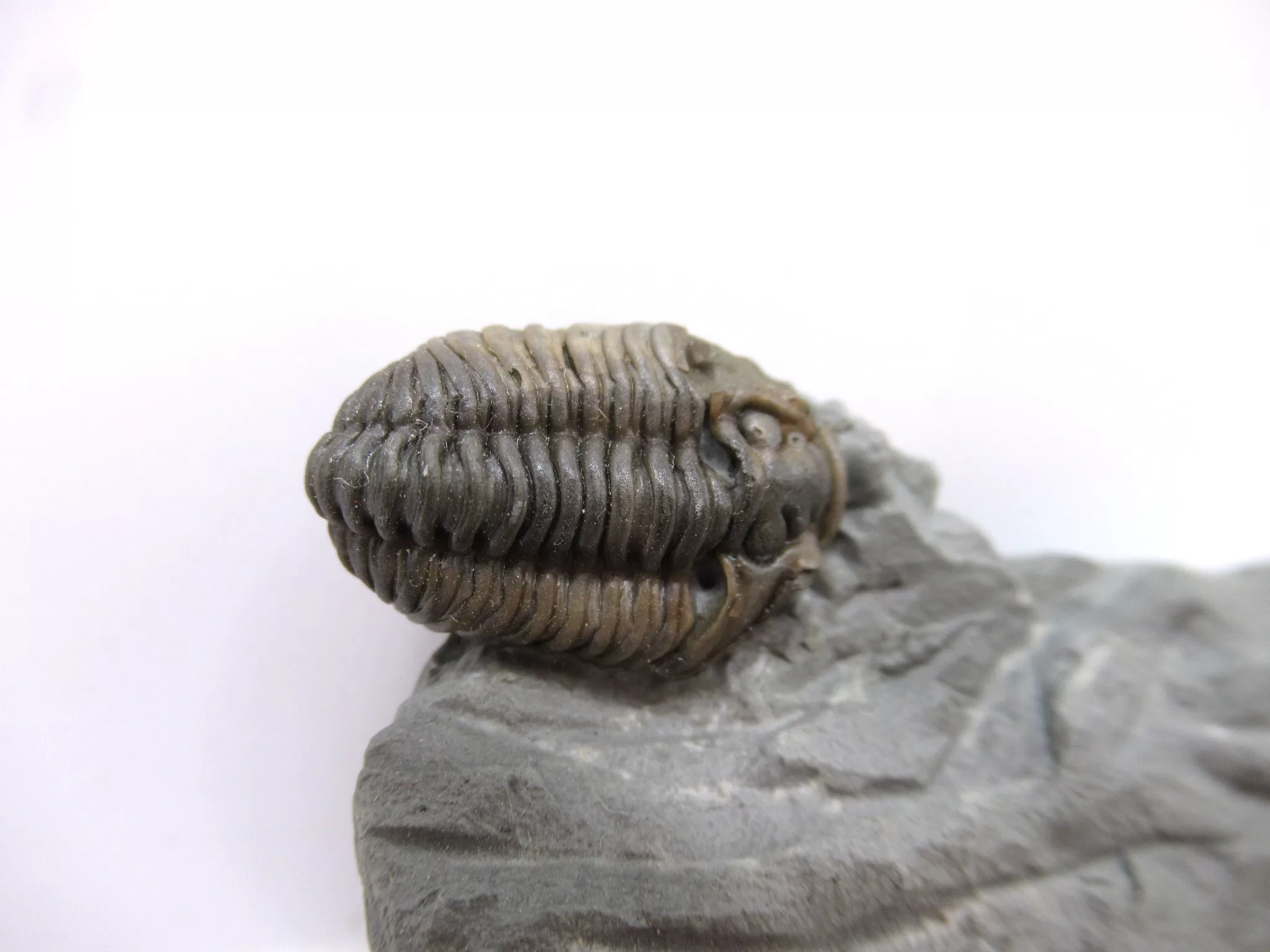
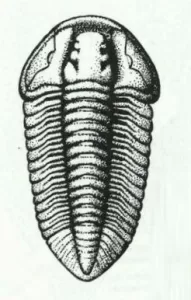
Flexicalymene Trilobite for Sale
- Flexicalymene (retrosa) trilobite
- Ordovician Age
- Richmond Formation
- Mt. Orb, Ohio
- This very nice specimen has been prepared with micro pneumatic tools and micro air abrasives and remains on the natural matrix it was found on. The trilobite itself measures .76″ long.
- More Trilobites for Sale
WHAT IS A FLEXICALYMENE
Flexicalymene is a genus of trilobites of the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina. Flexicalymene specimens can be mistaken for Calymene, Gravicalymene, Diacalymene and a few other Calymenina genera. They are used as an index fossil in the Ordovician. Ohio and North America are particularly known for being rich with Flexicalymene fossils. Species include F. meeki and F. retrorsa (Ohio, Kentucky and Indiana), F. granulosa (Ohio, Kentucky and Quebec), F. senaria (Quebec) and F. croneisi (Ontario).
WHAT IS A TRILOBITE?
Trilobites (meaning “three lobes”) are a fossil group of extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period (521 million years ago), and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic era before beginning a drawn-out decline to extinction when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetids died out. Trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 250 million years ago. The trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, roaming the oceans for over 270 million years.
WHEN WERE TRILOBITES ALIVE?
By the time trilobites first appeared in the fossil record, they were already highly diversified and geographically dispersed. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized exoskeleton, an extensive fossil record was left behind, with some 17,000 known species spanning Paleozoic time. The study of these fossils has facilitated important contributions to biostratigraphy, paleontology, evolutionary biology, and plate tectonics. Trilobites are often placed within the arthropod subphylum Schizoramia within the superclass Arachnomorpha (equivalent to the Arachnata), although several alternative taxonomies are found in the literature.
WHAT DID TRILOBITES EAT?
Trilobites had many lifestyles; some moved over the sea bed as predators, scavengers, or filter feeders, and some swam, feeding on plankton.