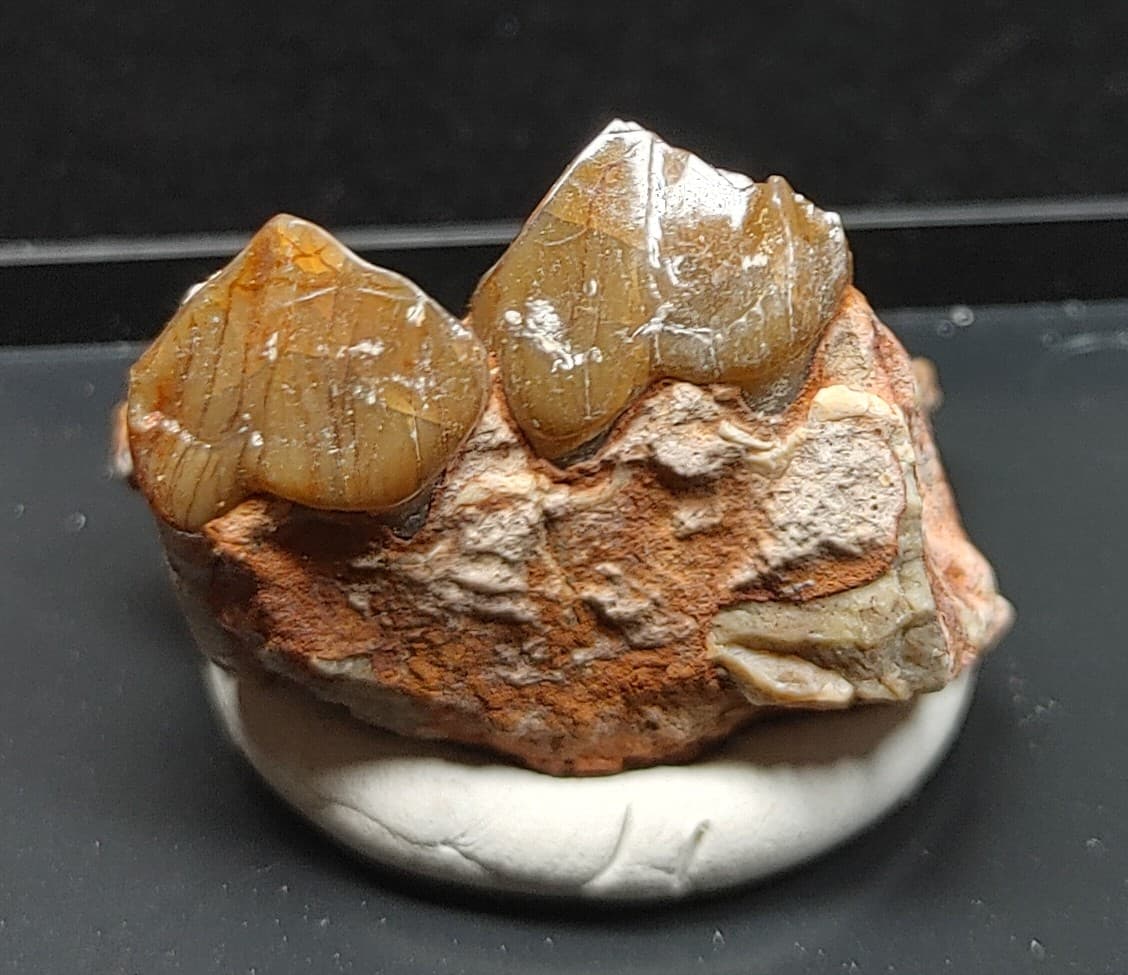
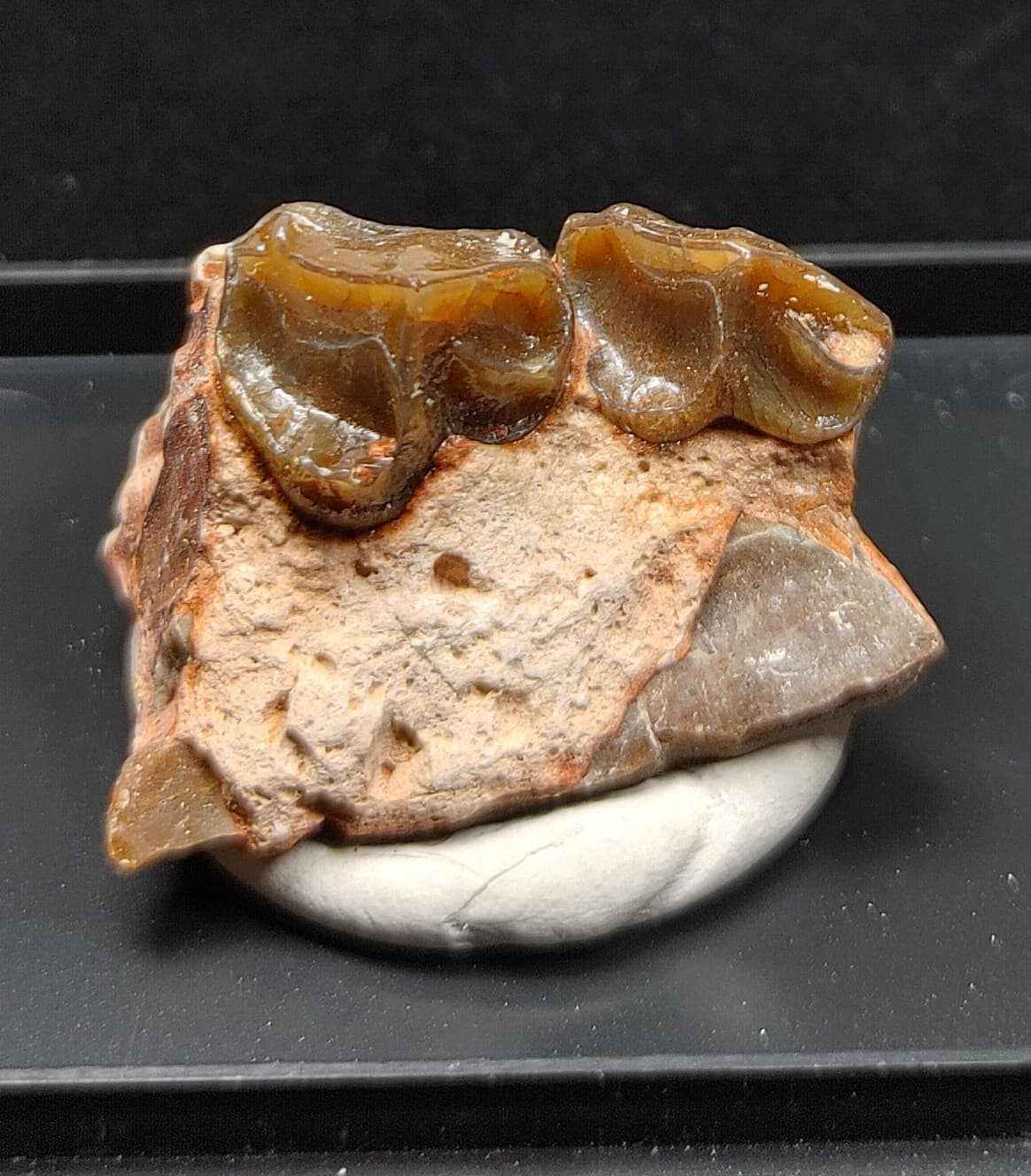
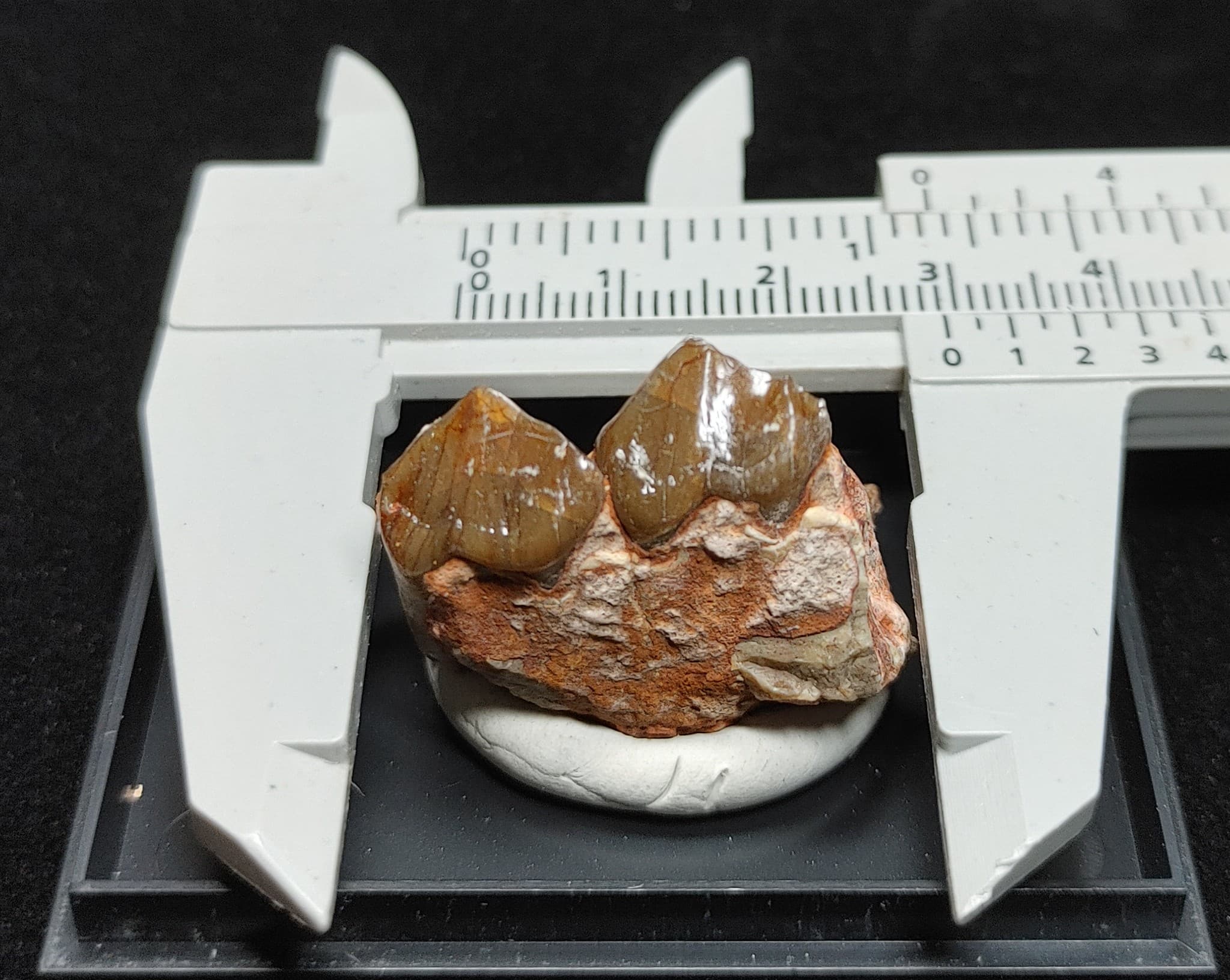
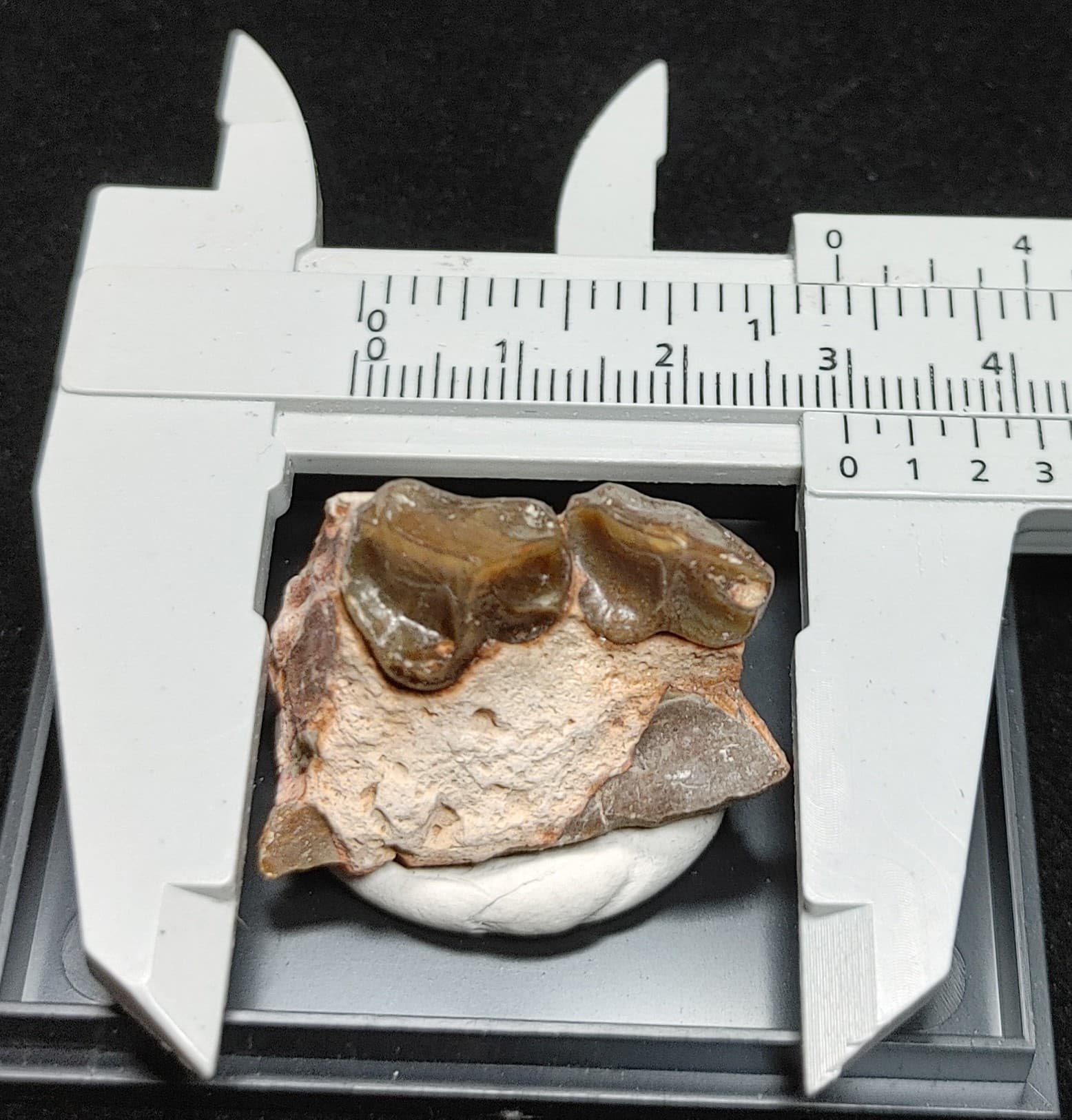
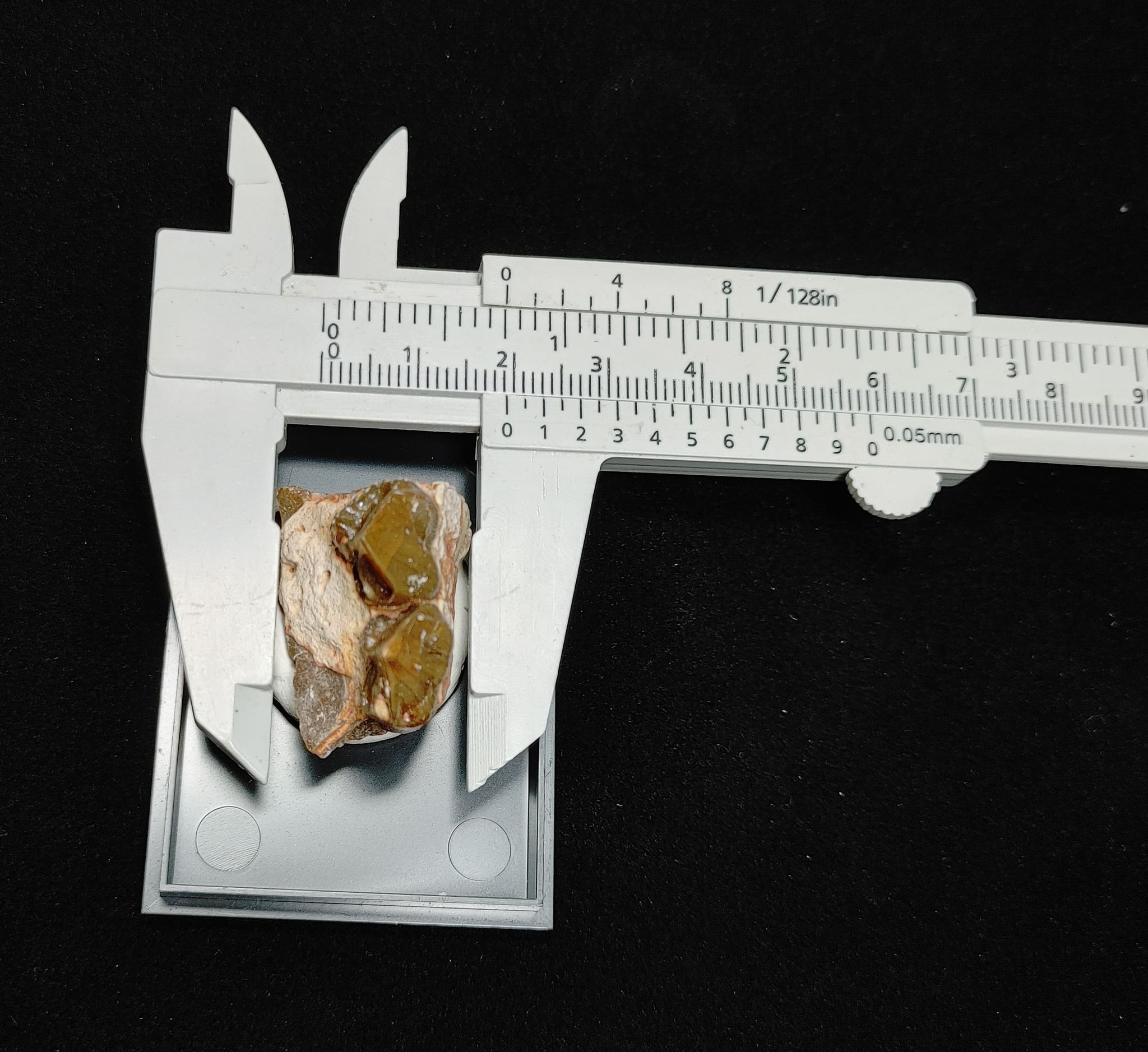
Description
- Oreodont Jaw
- Oligocene Age
- White River Formation
- Niobrara County, Wyoming
- See Specimen Pictures For Measurements
Merycoidodontoidea, sometimes called “oreodonts,” or “ruminating hogs”, is an extinct superfamily of prehistoric cud-chewing artiodactyls with short faces and fang-like canine teeth. As their name implies, some of the better known forms were generally hog-like, and the group was once thought to be a member of Suina, the pigs, peccaries and their ancestors, though recent work indicates they were more closely related to camels. “Oreodont” means “mountain teeth”, referring to the appearance of the molars. Most oreodonts were sheep-sized, though some genera grew to the size of cattle. They were heavy-bodied, with short four-toed hooves and comparatively long tails. The animals would have looked rather pig- or sheep-like, but features of their teeth indicate they were more closely related to camelids. They were most likely woodland and grassland browsers, and were widespread in North America during the Oligocene and Miocene.
The two families of oreodonts are the Merycoidodontidae (originally known as Oreodontidae) which contains all of the advanced species, and the Agriochoeridae, smaller, primitive oreodonts. Together they form the now-extinct suborder Oreodonta. Leptauchenia is an extinct goat-like genus of terrestrial herbivore belonging to the oreodont family Merycoidodontidae, and the type genus of the tribe Leptaucheniini. The genus was endemic to North America during theLate Oligocene (33.9—16.3 mya) and lived for approximately 17.6 million years. Because the eyes and nostrils were placed high on the head, it was long assumed that Leptauchenia was an aquatic, or semi-aquatic animal. However, because their fossils have never been found in floodplain deposits or river channels, and their abundance in fossil sand dunes, Donald Prothero suggests that they were desert-dwelling animals. According to Prothero’s interpretation, the high-placed eyes and nostrils served to filter out sand while burrowing, or while digging themselves free of sand dunes.