Fossil Jellyfish for Sale
Fossil Jellyfish for Sale – The oldest known fossils of jellyfish have been found in rocks in Utah that are from the Cambrian Period. The Cambrian Period is over 500 million years old.
Jellyfish are rarely fossilized because they have soft bodies with no bones. Jellyfish were carnivores eating planktonic organisms, crustaceans, small fish, and other jellyfish
We have fossil jellyfish for sale from the United States, Germany and Ukraine.
Showing all 17 results
-

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #24
$125.00 -

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #25
$125.00 -

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #26
$115.00 -

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #27
$125.00 -
Sold out!

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #28
$125.00 -
Sold out!

Nemiana simplex Precambrian Jellyfish from Ukraine #29
$125.00 -
Sold out!

Jurassic Solnhofen Jellyfish #6
$125.00 -
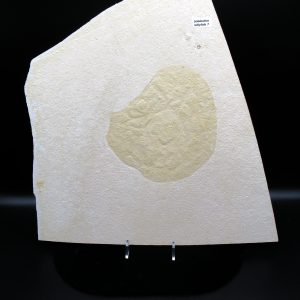
Jurassic Solnhofen Jellyfish #7
$125.00 -

Solnhofen Jellyfish #5
$160.00 -

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #2
$25.00 -
Sold out!

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #21
$25.00 -
Sold out!

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #22
$25.00 -

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #25
$25.00 -

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #28
$25.00 -

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #29
$25.00 -
Sold out!

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #7
$25.00 -

Mazon Creek Jellyfish Nodule #8
$25.00
- Buy Fossils
- Fossils for Sale
- Large Selection
- Great Prices and Great Selection
- Authenticity Guaranteed
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
- Your TRUSTED SOURCE SINCE 1997!
- Many more videos are available on our YouTube Channel.
Rare Windows Into Ancient Marine Ecosystems
Introduction

Fossil jellyfish are among the rarest and most scientifically valuable soft-bodied fossils on Earth. Unlike bones or shells, jellyfish lack hard tissues, making their preservation exceedingly unlikely. When fossilized, they provide exceptional insights into the evolution of early marine life, paleoenvironmental conditions, and the deep origins of Cnidaria—one of the oldest lineages of animals on the planet.
This article explores the science behind fossil jellyfish formation, their geological significance, major discoveries, and what these ancient organisms reveal about Earth’s biological history.
What Are Fossil Jellyfish?
Fossil jellyfish are impressions or mineralized remains of ancient medusozoans preserved in sedimentary rocks. These fossils typically record:
- The bell shape
- Tentacle traces
- Radial symmetry patterns
- Ripple or collapse structures from the soft body settling on sediment
Because jellyfish are composed of approximately 95–98% water, only rapid burial and exceptional sediment conditions allow them to fossilize.
How Do Jellyfish Fossilize?
- Rapid Burial in Fine Sediment
Most fossil jellyfish are preserved in fine-grained shale or sandstone, which captures delicate soft-tissue impressions before decay.
- Low-Oxygen Environments
Anoxic (oxygen-poor) conditions slow decomposition, allowing impressions to form.
- Early Diagenesis (Rapid Mineralization)
Minerals such as silica, phosphate, or iron may coat the organic structures, stabilizing the shape before it collapses.
- Exceptional Preservation Conditions (Lagerstätten)

Many fossil jellyfish come from sites known for extraordinary fossil preservation, such as the Burgess Shale or Ediacara Hills.
Geological Age and Evolutionary Significance
Fossil jellyfish stretch back more than 550 million years, making them crucial for understanding animal evolution.
Ediacaran Period (635–541 Ma)
The earliest possible jellyfish-like fossils appear in this era. These specimens show radial symmetry consistent with early cnidarians.
Cambrian Period (541–485 Ma)
Sites such as the Burgess Shale and Chengjiang Biota reveal distinctive medusoid forms with preserved bells and tentacles.
Jurassic & Cretaceous Periods
Younger fossil jellyfish from Utah, Wisconsin, and Europe show remarkable detail due to rapid burial in shallow marine sediments.
Major Fossil Jellyfish Discoveries
🟦 1. The Utah Medusae (Middle Cambrian)

Utah’s Marjum and Wheeler formations have produced some of the best-known fossil jellyfish, with clear bell structures and tentacle impressions.
🟧 2. Ediacaran Medusozoans
The Ediacara Hills of Australia contain some of the earliest known jellyfish-like fossils—important for understanding the origins of animal multicellularity.
🟩 3. La Voulte-sur-Rhône (Jurassic)
This French Lagerstätte is famous for its soft-tissue preservation, including remarkable fossilized gelatinous organisms.
What Fossil Jellyfish Reveal About Ancient Oceans
- Early Animal Evolution
Fossil jellyfish help confirm that Cnidaria diverged early in the tree of life, predating the Cambrian Explosion.
- Paleoenvironmental Conditions
Their presence indicates:
- Calm, low-oxygen seafloor conditions
- Fine sediment deposition
- Minimal bioturbation (little disturbance by other organisms)
- Ecosystem Structure
Fossil jellyfish suggest complex food webs existed hundreds of millions of years ago, with predators, prey, and planktonic communities already well established.
SEO Section: Frequently Asked Questions
Are fossil jellyfish rare?
Yes—exceptionally. Their soft bodies usually decay before burial, so only unique environmental conditions allow fossilization.
How old is the oldest fossil jellyfish?
Some candidates date to ~550 million years, potentially making jellyfish among the earliest animal groups.
Where are fossil jellyfish found?

Notable localities include:
- Utah, USA
- Wisconsin, USA
- Ediacara Hills, Australia
- Chengjiang, China
- Burgess Shale, Canada
Do fossil jellyfish show tentacles?
Sometimes. Tentacles are much harder to preserve, but impressions or filament traces appear in several Lagerstätten.
Buy Fossils from Prehistoric Fossils with Confidence. Authenticity Guaranteed!