Cabochons for Sale | Jewelry or Meditation
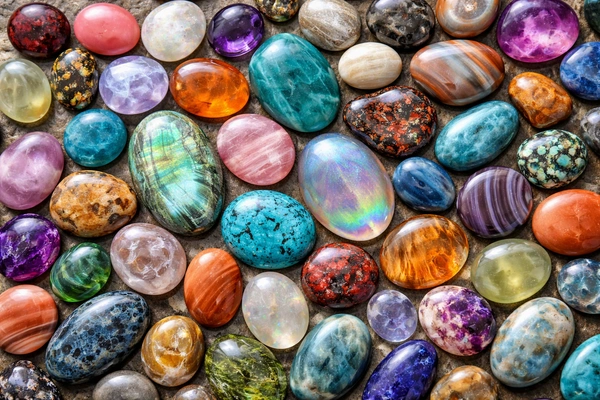
Cabochons for Sale for Jewelry or Meditation. | A cabochon is a gemstone that has been shaped and polished, as opposed to faceted. | The resulting form is usually a convex (rounded) obverse with a flat reverse. | Cabochon was the default method of preparing gemstones before gemstone cutting developed
Buy Cabochons with Confidence. Your Trusted Source Since 1997. Authenticity Guaranteed
Showing all 35 results
- Buy Cabochons Bookends
- Genuine Gem Cabochons for Sale
- Large Selection
- Great Prices and Great Selection
- Authenticity Guaranteed
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
- Your TRUSTED SOURCE SINCE 1997!
- Many more videos are available on our YouTube Channel.
Cabochon Gemstones: Scientific Properties, Geological Formation, and Lapidary Applications
Abstract
Cabochon gemstones represent one of the oldest and most scientifically significant gemstone cutting styles. Unlike faceted gems, cabochons are shaped and polished into smooth, convex forms that emphasize optical phenomena, mineral structure, and surface-based light interactions.
What Is a Cabochon?
A cabochon is a gemstone cut with a domed top and flat or slightly curved base, lacking facets. This cutting style is primarily used for opaque to translucent materials or gemstones exhibiting surface-dependent optical effects.
From a gemological standpoint, cabochon cutting is selected when:
- Internal transparency is limited
- Optical phenomena depend on surface curvature
- Structural integrity is improved without faceting
Cabochons are commonly used for minerals such as jade, opal, turquoise, moonstone, labradorite, and agate.
Geological Formation of Cabochon Materials
Cabochon gemstones originate from diverse geological environments, including:
Igneous Processes
- Feldspar minerals (e.g., moonstone, labradorite)
- Obsidian (volcanic glass)
Sedimentary Processes
- Turquoise (secondary copper mineralization)
- Malachite (carbonate precipitation)
Metamorphic Processes
- Jadeite and nephrite jade
- Lapis lazuli (contact metamorphism)
The microcrystalline or fibrous structures common in these materials make faceting ineffective, reinforcing the use of cabochon cutting.
Optical Phenomena Unique to Cabochons
Cabochon cutting is scientifically essential for displaying several gemstone optical effects:
Adularescence
Observed in moonstone due to light scattering between feldspar layers.
Asterism
Star effects in sapphire and ruby caused by oriented rutile inclusions.
Chatoyancy
“Cat’s eye” effect produced by parallel fibrous inclusions.
Opalescence
Light diffraction in hydrated silica spheres within opal.
The curved surface of a cabochon optimizes light reflection and refraction, making these effects visible.
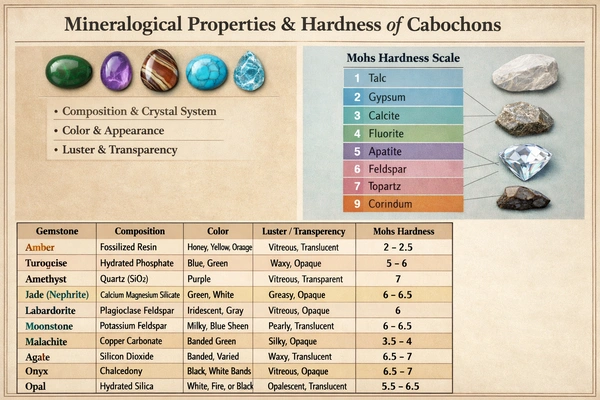
Mineralogical Properties and Hardness
Cabochon gemstones span a wide range of physical properties:
| Mineral | Mohs Hardness | Transparency |
| Opal | 5.5–6.5 | Translucent |
| Jadeite | 6.5–7 | Opaque |
| Quartz (Agate) | 7 | Translucent |
| Turquoise | 5–6 | Opaque |
Lower hardness minerals benefit from cabochon cutting because:
- Stress points are minimized
- Durability is improved
- Surface wear is reduced compared to faceted edges
Lapidary Science: Why Cabochon Cutting Matters
From a materials science perspective, cabochon cutting:
- Preserves crystal integrity
- Reduces cleavage-related breakage
- Enhances color zoning and banding
- Improves yield from irregular rough material
Lapidaries typically use progressive silicon carbide or diamond abrasives, finishing with cerium or tin oxide polishing compounds depending on mineral chemistry.
Applications in Jewelry and Industry
While cabochons are widely used in fine jewelry, their applications extend further:
- Archaeological replicas and museum conservation
- Watchmaking (sapphire cabochon crowns)
- Scientific reference specimens
- Energy-dispersive spectroscopy samples (flat base advantage)
Their shape also allows secure bezel settings, improving long-term wearability.
Conclusion
Cabochon gemstones are not merely aesthetic choices but scientifically informed solutions to mineral structure, optical physics, and material durability. Their continued relevance in gemology, jewelry, and scientific study underscores the importance of understanding cabochon cutting from both a geological and technical perspective.
Buy Cabochons with Confidence. Your Trusted Source Since 1997. Authenticity Guaranteed